The system will only grab the data of the past 7 days on the second day after the shop has been authorized.
For example, You authorized the store on November 9. Our system will start counting the data of the previous 7 days at 00:00 on November 10 (that is, the data on November 3, November 4, November 5, November 6, November 7, November 8, and November 9).
Please confirm whether you have ever modified the product price or set a promotional price. If not, please contact us.
Because the system doesn't run data in real-time but will only do this in the early morning, around 1:00 am. And due to the delay of the API interface feedback, orders on the previous day may have not been fully synchronized from the marketplace to Bigseller. If you encounter this situation, we suggest you check the data the next day.
For example: after the 11.11 big promotion, the number of orders on November 12th may be wrong. It is recommended that you check the data again on November 13th.
If does, the same order number will correspond to multiple tracking numbers. One tracking number will be counted as one package when the system calculates the Outbound Package Qty.
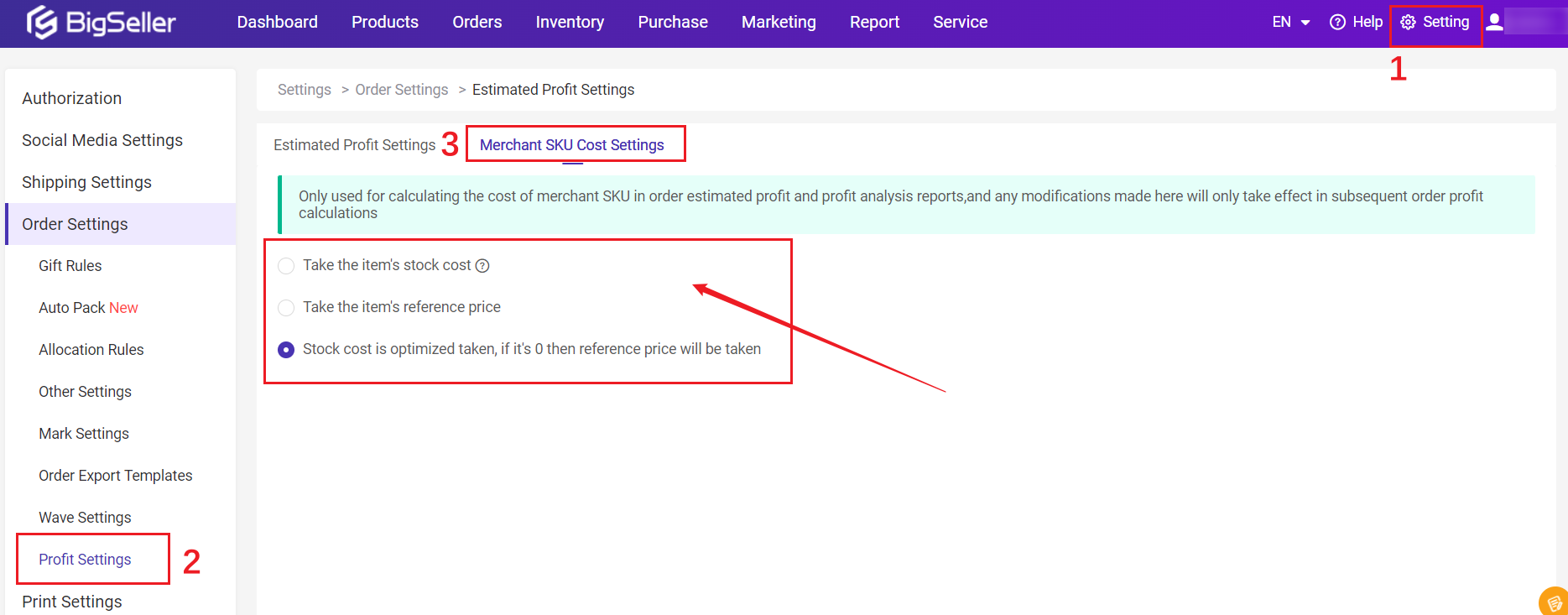
① Take the item's stock cost: system will take the cost price of the merchant SKU by default. If the cost price is 0, it is taken as 0.
② Take the item's reference price: system will take the reference price of the merchant SKU by default. If the reference price is 0, it is taken as 0.
③ Stock cost is optimized taken, if it's 0 then reference price will be taken: system will take the cost price of merchant SKU. If the cost price is 0, the reference price is taken; If the reference price is 0, it is taken as 0.
Stats Combination SKU by Single SKU: The combination SKUs will not be displayed in the list. The Valid Sales Quantity and Valid Sales of the combination SKUs will be allocated to the single SKUs and then sorted.
*When switching options, please refresh the list data.
How to Stats Combination SKU by Single SKU
1. Sales, Valid Sales, Refunds, Cancel Amount:
▶ Allocate according to the quantity of single SKUs in the combination SKU and the cost allocation ratio
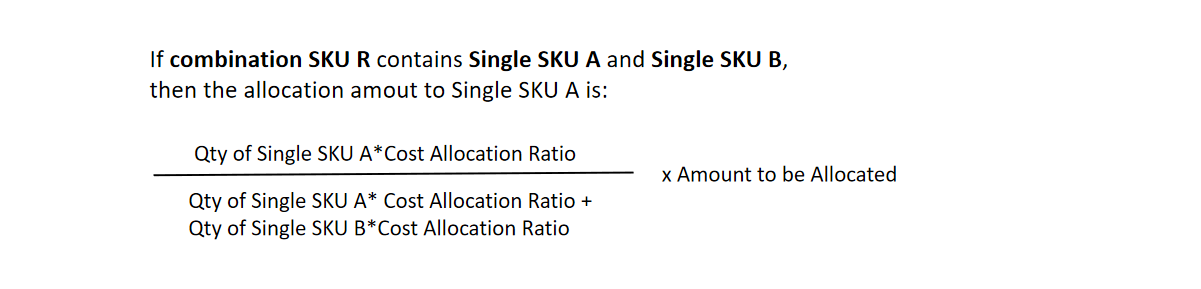
Notes
① The system will retain two decimal places;
② The allocated amount of the last SKU = Total Amount - Amount Already Deducted;
③ If the qty of single SKUs in the combination SKU or the cost allocation ratio changes, it will not affect the previously allocated data, but will only affect the new order data after the change.
For example:
Combination SKU [Ball 001] consists of two [red balls] and three [green balls]. The cost allocation ratio for the red balls is 1, and the cost allocation ratio for the green balls is 5.
In one order, the valid sales of combination SKU [Ball 001] is 10. At this time, the valid sales of the red ball and the green ball are:
Valid Sales of Red Ball = 2*1/(2*1+3*5)*10= 1.17
Valid Sales of Green Ball = 10-1.17= 8.83
2. Sales Volume, Refund Volume, Cancel Products:
▶ Sales quantity of Single SKUs= Composition quantity of single SKUs * Sales quantity
For example, in order [001], there is a combination SKU [Ball 001] (consisting of 2 blue balls and 3 green balls), and the sales volume is 2.
At this time, the sales volume of a single SKU are:
Blue ball: 2*2= 4, Green ball 3*2= 6
3. Orders, Package Quantity, Refund Orders, Cancel Orders:
▶ Directly add to the single SKUs of the combination SKU based on the number of combination SKUs.
For example. in order [001], there is a combination SKU [Ball 001] (consists of 2 blue balls and 3 green balls). That is, the order quantity of the combination SKU is 1.
So when combination SKU data is counted on the single SKUs, the order quantity of blue balls is increased by one, and the order quantity of green balls is also increased by one.